Raster Vs Vector
There are two main types of graphic - Raster and Vector.
Raster images are made up of pixels, whereas vector images are made from points being placed to form geographical objects (ie lines and shapes).
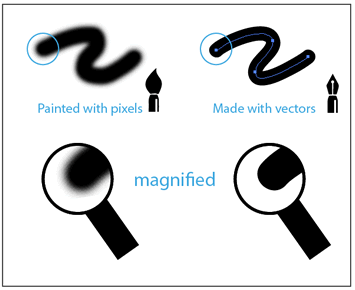
Below you can see a comparison of raster and vector images.

Because vector images are based on mathematics, they do not lose any quality no matter how large you make the image.
Raster images, on the other hand will start to pixelate as soon as you start to increase their size, as show below.

The reason raster images pixelate when enlarged is because they are made up of rows and columns
of very small dots (pixels). When viewed at their original size, the human eye is not able to
perceive individual pixels in a raster image.
However when you enlarge it, the pixels start to become more apparent.
What are raster images used for?
The most common type of raster images are photographs. All photographs are made up of pixels.
However it's not only photographs that are raster images.
Most web graphics such as logos, banners and icons are raster images as it most vectors file formats
are not supported by web browsers.
Whilst raster images are not ideal for all types of graphics,
as long as the image doesn't need to be scaled up to any large degree, then they work well.
- Popular raster image files - jpg, jpeg, png, psd, tif, pdf
- Popular raster programs - Photoshop, Paint, GIMP
- Popular raster image uses - photographs, graphics with a lot of effects
What are vector images used for?
Vector images are commonly used in graphic design to create logos, mascots and other web graphics.
Vector images have a very distinctive and clean look, which makes them perfect for these types of a
applications.
The reason that vector images are often used for logo design is because they're versatile and hence very easy to
edit as well as scale up at any time. Let's say for example, a company has a logo designed as a vector file.
They might only want to use it on their website and business card at first but as the business grows there's a
good chance they'll need to use it on t-shirts, posters and other types of products that require it to be made
larger without loss of quality. This is where vector images shine.
As you can see from the pictures below, no matter how much a vector logo is increased in size, it doesn't lose any quality.



- Popular Vector image files - ai, eps, cdr, pdf
- Popular Vector programs - Illustrator, Corel Draw
- Popular Vector image uses - logos, web graphics, engraving, cartoon graphics, crests, printing
Which is better?
Which type of image is better all depends on how it's going to be used.
For creating things like photo manipulations and digital paintings, then raster images are the obvious choice.
For graphics that need to be scalable as well as easily edited then vectors are ideal.
Can you increase a raster image without loss of quality?
It is possible to increase the size of a raster image whilst avoiding pixelation within reason.
To understand how this works it's necessary to understand what PPI is and how it relates to raster images.
PPI is the Pixels Per Inch within an image. The more pixels there are per inch, the better the quality of the picture and the more you can increase the size without loss of quality.
In Photoshop, you can manually increase the PPI of an image but the results are not always ideal.
This is because photoshop will randomly add pixels to increase the PPI.
Whilst this might appear to give the image a higher resolution to the casual eye, it's still far from the infinite scalability you get with vector images.
Can you convert a raster image to a vector?
The short answer to this question is - yes. Provided the raster image is a graphic rather than a photograph, it's possible to create it as a vector image.
The best way to achieve this is by manually tracing the original image in a vector program such as Illustrator. This way you can manipulate and recolour the image as needed.
Below is a pictorial showing the types of vector graphics you can achieve using different techniques.
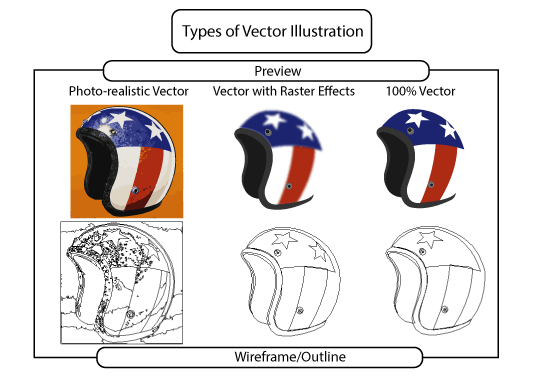
1. Photo-realistic Vector
The photo-realistic helmet was traced in Illustrator and maintains a good amount of detail from the original photograph. It's possible to print a photo-realistic vector like this digitally, although the complexity of the wireframe makes it unsuitable for engraving or vinyl-cut signs.
2. Vector with Raster Effects
The second image shows the helmet after it's been manually traced in Illustrator and the main shapes have been filled with one tone of colour and had a raster effect (gaussian blur) applied. Whilst this image was created in Illustrator, it's not 100% vector, which means it cannot be scaled up without loss of quality.
3. 100% Vector
This is a 100% vector image that can be scaled up infinitely without any loss of quality.
It's made up completely of vector shapes and has one tone of colour within each shape. Because all the line work is created as a vector, it's suitable for printing at any size as well as being used for engraving and vinyl-cut signs.
Tracing Logos
Below you see how a previously pixelated logo was recreated as a vector in Illustrator. The difference is stark, as you can see all the jagged lines have been completely eliminated. This is where image to vector conversion really excels and why vectors are commonly used in logo design.

Printing Considerations
To figure out what size you can print a raster image at without loss of quality you have to take a couple of factors into account.
The first is the PPI required by your printer. The second is how large the image is on your screen.
For example if the width of the image is 1000 pixels and your printer requires 300PPI for printing, then the maximum size you could print it without loss of quality is 3.3 inches (1000/300 = 3.3)
With a vector image, you don't have to worry about PPI or file sizes, since you can enlarge it to any degree and print it without loss of quality.
DPI Vs PPI
DPI - Dots Per Inch
The DPI is determined by your printer and is the amount of ink dots that will be placed on each pixel of your image.
PPI - Pixels Per Inch
With raster images, the PPI will be determined by the device you create the picture with, whether it's a camera, scanner or graphics program.
The PPI can be manually edited by using software such as Photoshop.
Summary
To help summarise, let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of raster and vector images respectively.
Raster Advantages
- Great for editing photos
- Great for digital paintings
- Allows for smoother blends and more tones of colour
Raster Disadvantages
- Loss of quality when scaled up
- File sizes are typically much larger
- More difficult to print without loss of quality
Vector Advantages
- Perfect for graphics such as logos, mascots and icons
- Infinitely scalable
- Easy to edit
- Smaller file sizes
Vector Disadvantages
- Requires expertise with graphic design
- Conversion can be time-consuming
- Not good for editing photos
If you have a raster that you need to converted to a Vector EPS then please visit our homepage.
(Prices start from just £19.99)
(Prices start from just £19.99)
 My Basket
My Basket ( 020 8050 1445 )
( 020 8050 1445 )
